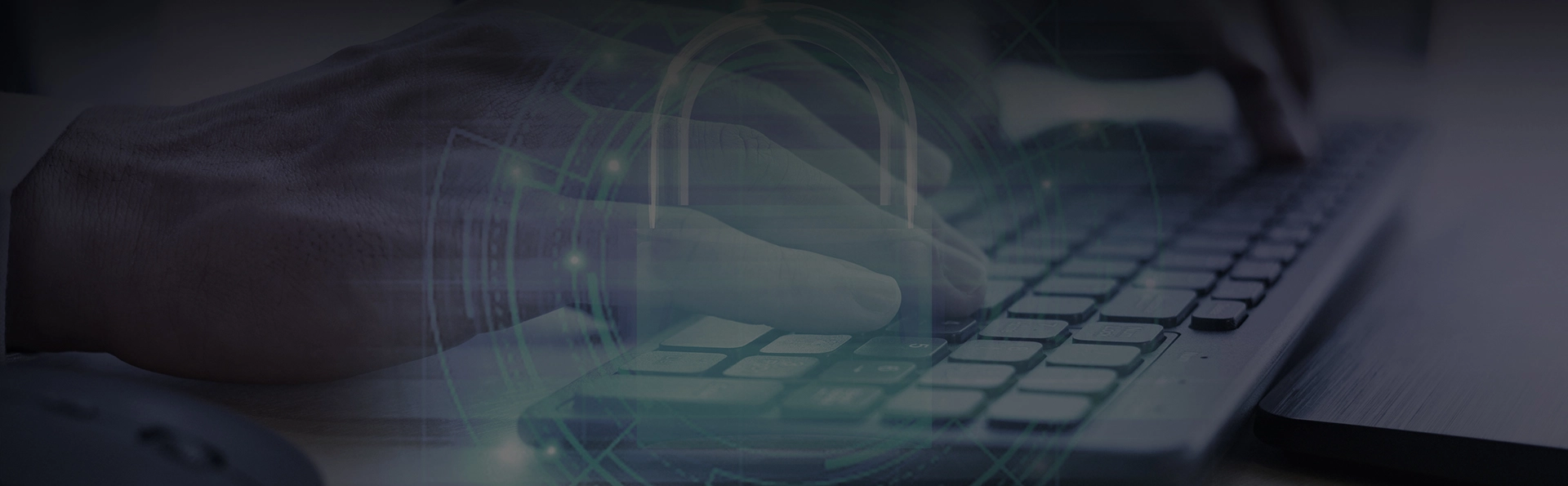

Blockchain technology is a comprehensive innovative application model of point-to-point transmission, consensus mechanism, encryption algorithm, distributed data storage and other technologies.
The security of the blockchain wallet mainly depends on the protection of the private key. Safe practices include choosing a trusted wallet provider, making sure the wallet software is up to date, using strong passwords and two-factor authentication, regularly backing up private keys, and storing them on a secure offline device. Also, avoid entering private keys in untrusted websites or applications to prevent phishing attacks.

A 51% attack refers to an attacker who controls more than 51% of the total computing power of the blockchain network, thereby being able to manipulate transaction records. To prevent such attacks, the blockchain network needs to have sufficient decentralization and distributed computing power distribution. In addition, some consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, can increase the cost and difficulty of attacks.


